12 月 . 04, 2024 09:34 Back to list
однофазный распределительный блок питания
Understanding Single-Phase Distribution Power Units
In modern electrical systems, effective power distribution is paramount. One such system that plays a crucial role in power management is the single-phase distribution power unit. While it may seem simple in design, its impact on electrical efficiency and stability cannot be overstated. This article explores the characteristics, applications, advantages, and challenges of single-phase distribution power units.
What is a Single-Phase Distribution Power Unit?
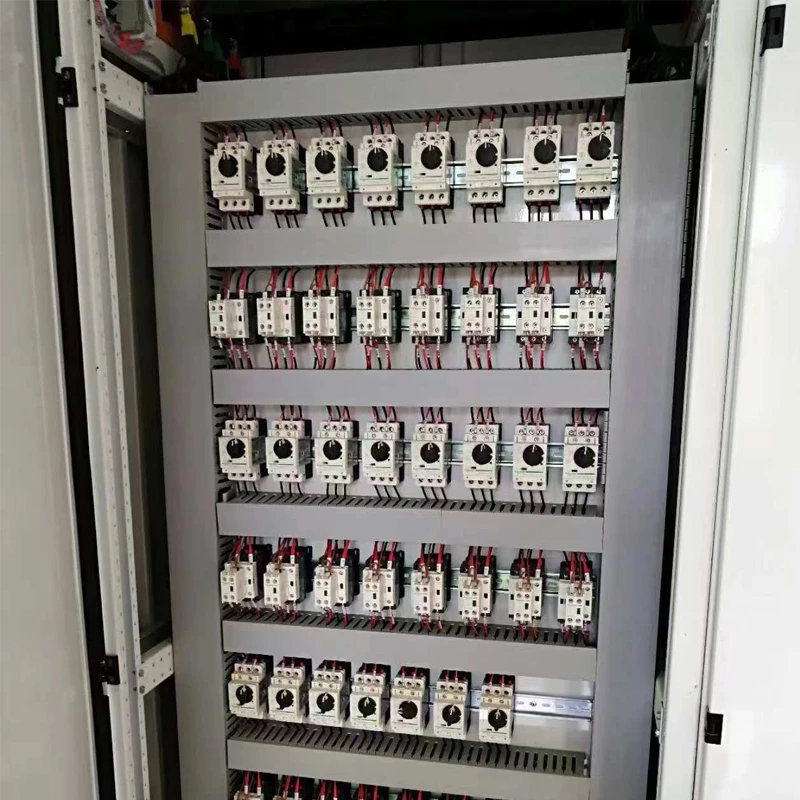
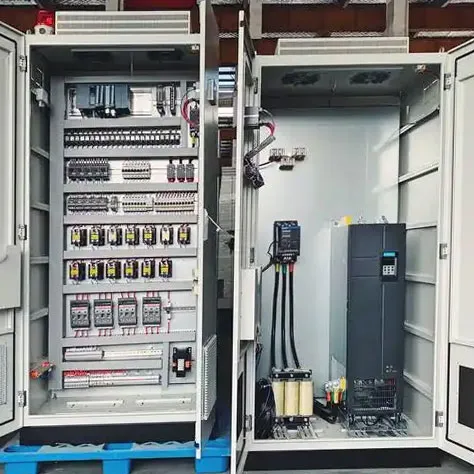
A single-phase distribution power unit is designed to deliver electrical power to various devices and systems using a single alternating current (AC) phase. It typically consists of essential components such as transformers, circuit breakers, distribution blocks, and switches, facilitating the smooth flow and distribution of electrical energy from its source to end-use applications.
Single-phase systems are predominantly used in residential and light commercial contexts, where the demand for power is relatively low compared to industrial settings. They usually operate at voltages like 120V or 240V, which aligns well with the electrical requirements of household appliances, lighting, and small machinery.
Characteristics of Single-Phase Systems
Single-phase distribution systems are characterized by their simplicity and user-friendliness. They involve a single conductor and a neutral return path, making the installation and maintenance relatively straightforward. This configuration reduces the complexity associated with three-phase systems, which require greater expertise and precision in handling.
Moreover, these systems tend to be more cost-effective. The need for fewer components translates to lower initial costs, making single-phase distribution power units an attractive option for many residential setups and small businesses.
.
Single-phase distribution power units find extensive use in various applications. Residential homes predominantly use these systems to power lights, heating systems, refrigerators, and other appliances. In small commercial enterprises, single-phase units may supply power to computers, point-of-sale systems, and light manufacturing equipment.
однофазный распределительный блок питания

Given their lower power demands, these systems are favored in environments where high power loads are not a requirement. They can serve standalone installations or be part of a more complex power distribution network that includes three-phase systems when higher loads need to be managed.
Advantages
One of the significant advantages of single-phase distribution power units is their ease of implementation. With fewer components in their design, installation is typically quicker, reducing downtime and labor costs. The equipment and materials needed for single-phase systems are also more readily available, ensuring a smooth procurement process.
Additionally, single-phase units are often quieter and less prone to vibration issues, making them a practical choice for residential areas. Their lower power requirements can lead to energy savings, and advanced technologies in energy efficiency ensure that even single-phase systems contribute positively to overall energy management.
Challenges
Despite these advantages, single-phase distribution power units do have their drawbacks. One notable limitation is their capacity to handle high loads. In applications where substantial power is necessary, the single-phase system may not suffice, necessitating a transition to a three-phase system, which can complicate planning and implementation.
Moreover, power quality issues, such as voltage fluctuations, can be more pronounced in single-phase systems. Adding capacitors or other power factor correction devices may be necessary to mitigate these problems.
Conclusion
Single-phase distribution power units are integral to efficient power distribution in residential and small commercial applications. Their straightforward design, cost-effectiveness, and simplicity make them a preferred choice for many users. However, understanding their limitations is essential when planning an electrical system to ensure that power demands are adequately met without compromising quality and efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, advancements in single-phase systems will likely address many current challenges, further solidifying their role in the ever-evolving landscape of electrical power distribution.
-
Why Steel Mills Rely on FODA’s High-Temperature Cylindrical Roller Bearings?
NewsApr.10,2025
-
What is a Plain Bearing? A Complete Guide to Design & Functionality
NewsApr.10,2025
-
Thrust Ball Bearings vs. Tapered Roller Bearings: FODA’s Performance Comparison
NewsApr.10,2025
-
The Engineering Behind FODA Thrust Ball Bearings: Precision for High-Speed Applications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
No More Compromises: Get Precision-Engineered Custom Bearings Tailored to Your Exact Specifications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
In-Depth Analysis: Application Differences of Different Types of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
NewsApr.10,2025
Products categories