12 月 . 04, 2024 09:28 Back to list
lógica de control de procesos
Understanding Process Control Logic
Process control logic is a fundamental component in the design and operation of various industrial systems. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that processes function effectively and efficiently, embodying a framework that governs how operations are managed in manufacturing, chemical processing, water treatment, and other automated environments.
At its core, process control logic can be understood as the set of rules and algorithms that dictate how a process responds to changes in input variables. This logic allows for the monitoring and adjustment of systems to maintain desired outputs while minimizing inefficiencies and errors. The implementation of process control logic not only enhances productivity but also ensures product quality and safety.
Components of Process Control Logic
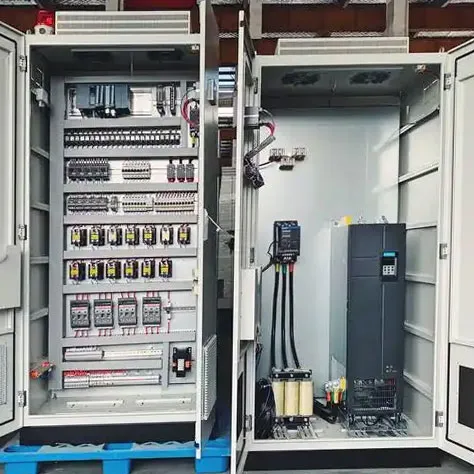
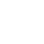
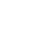
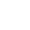
1. Sensors and Inputs The first step in process control logic involves gathering data through sensors. These sensors monitor various parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and chemical concentrations. The data collected serves as real-time inputs into the control system.
2. Control Algorithms Once data is collected, it is processed by control algorithms. These algorithms are mathematical functions designed to interpret the data and make decisions based on predefined conditions. Common control methods include PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control, which adjusts outputs based on error values (the difference between desired and actual performance), and more complex algorithms used in advanced control systems.
3. Actuators and Outputs After processing the input data and applying the control algorithms, the system issues commands to actuators. Actuators are devices that physically alter the state of a system, such as valves, pumps, and motors. The control logic dictates how and when these devices operate, ensuring the process remains within desired parameters.
4. User Interface Modern process control systems often feature user interfaces that allow operators to monitor performance and adjust settings manually if necessary. These interfaces display real-time data visualizations and alerts to indicate system status and performance deviations.
lógica de control de procesos

Importance of Process Control Logic
The importance of process control logic can be observed across various industries. In manufacturing, for instance, precise control over processes reduces waste and energy consumption, leading to cost savings and enhanced sustainability. In chemical processing, effective control logic is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with regulatory standards, preventing accidents caused by uncontrolled reactions or deviations from safe operating conditions.
Moreover, the digital transformation in process control, including the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence), has opened up new possibilities. Smart sensors and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, allowing for predictive maintenance and optimization of processes. This shift enables industries to not only react to changes but also to anticipate issues before they arise, resulting in more resilient and adaptive systems.
Challenges in Implementing Process Control Logic
Despite its advantages, the implementation of process control logic is not without challenges. One significant challenge is the complexity of designing algorithms that can handle the myriad of variables that influence a process. This complexity often requires specialized knowledge and skills in process engineering, programming, and data analysis.
Additionally, systems must be regularly maintained and updated to accommodate changes in processes or technological advancements. Failure to do so can lead to outdated systems that fail to perform optimally or safely.
Conclusion
In conclusion, process control logic is an essential aspect of modern industrial operations, providing the structure needed to ensure processes run smoothly and efficiently. By understanding the components and significance of process control logic, organizations can better equip themselves to face the challenges of regulation, safety, and efficiency in an ever-evolving technological landscape. As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, the role of process control logic will only grow, paving the way for smarter and more sustainable operational practices.
-
Why Steel Mills Rely on FODA’s High-Temperature Cylindrical Roller Bearings?
NewsApr.10,2025
-
What is a Plain Bearing? A Complete Guide to Design & Functionality
NewsApr.10,2025
-
Thrust Ball Bearings vs. Tapered Roller Bearings: FODA’s Performance Comparison
NewsApr.10,2025
-
The Engineering Behind FODA Thrust Ball Bearings: Precision for High-Speed Applications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
No More Compromises: Get Precision-Engineered Custom Bearings Tailored to Your Exact Specifications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
In-Depth Analysis: Application Differences of Different Types of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
NewsApr.10,2025
Products categories