12 月 . 13, 2024 14:44 Back to list
robot de soldadura de cuatro ejes basado en plc
Four-Axis Welding Robot Based on PLC Technology
In the landscape of modern manufacturing, automation has become a pivotal force driving productivity, precision, and efficiency. One of the cornerstones of this automation realm is the emergence of robotic systems, particularly welding robots. Among various configurations, four-axis welding robots have garnered significant attention due to their unique balance between flexibility and control. This article explores the capabilities, applications, and advantages of four-axis welding robots that utilize PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) technology.
Understanding Four-Axis Welding Robots
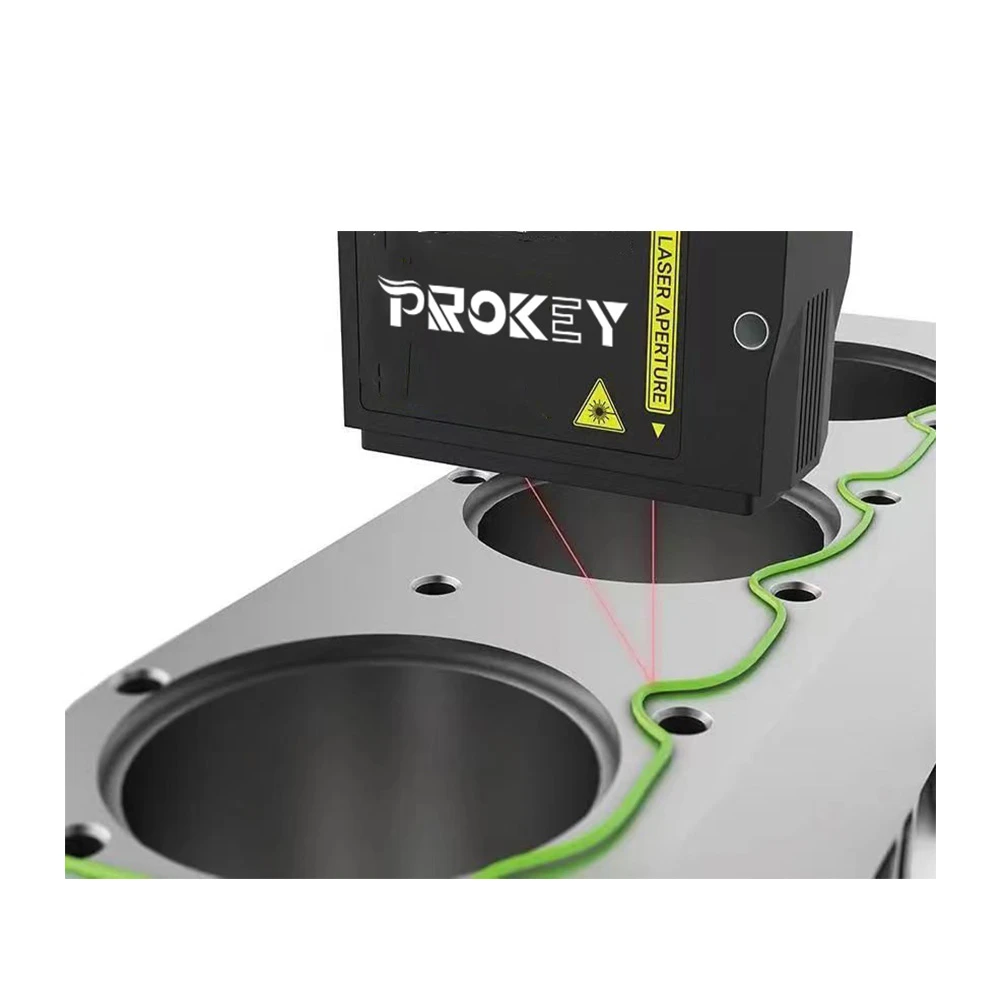
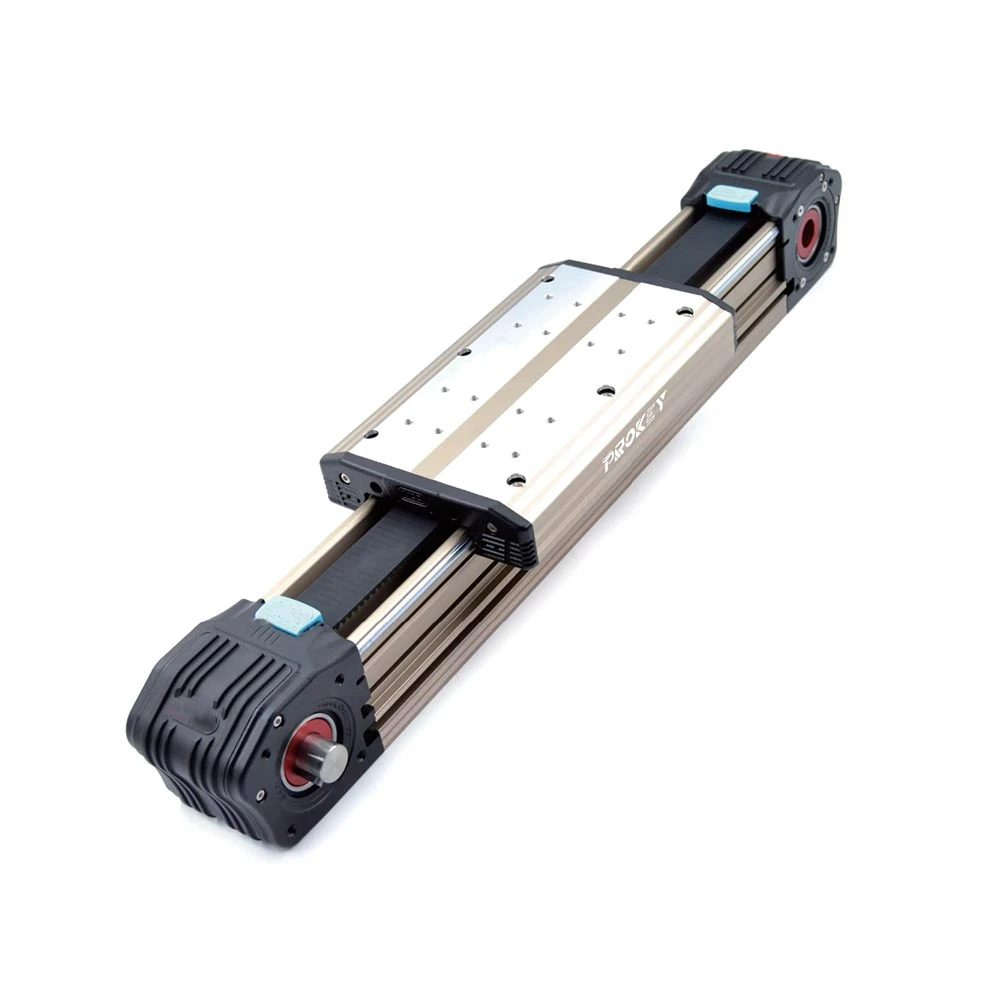
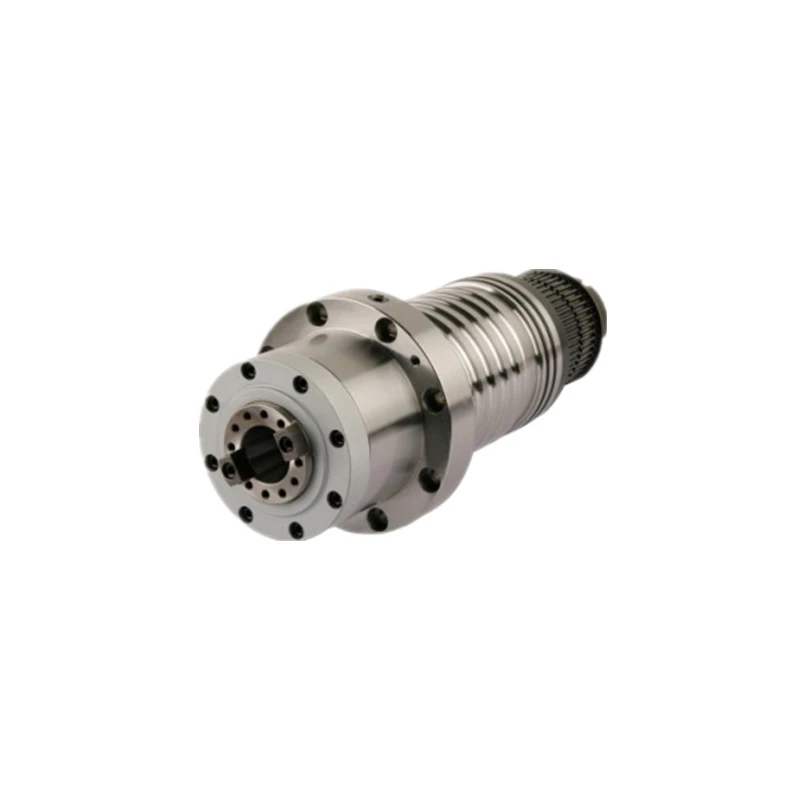
A four-axis welding robot is a type of robotic arm that employs four degrees of freedom to perform welding tasks. These axes typically consist of a linear movement along the X, Y, and Z coordinates, paired with a rotational movement that allows for precise positioning of the welding nozzle. The integration of PLC technology enhances the capabilities of these robots by providing advanced control and automation features.
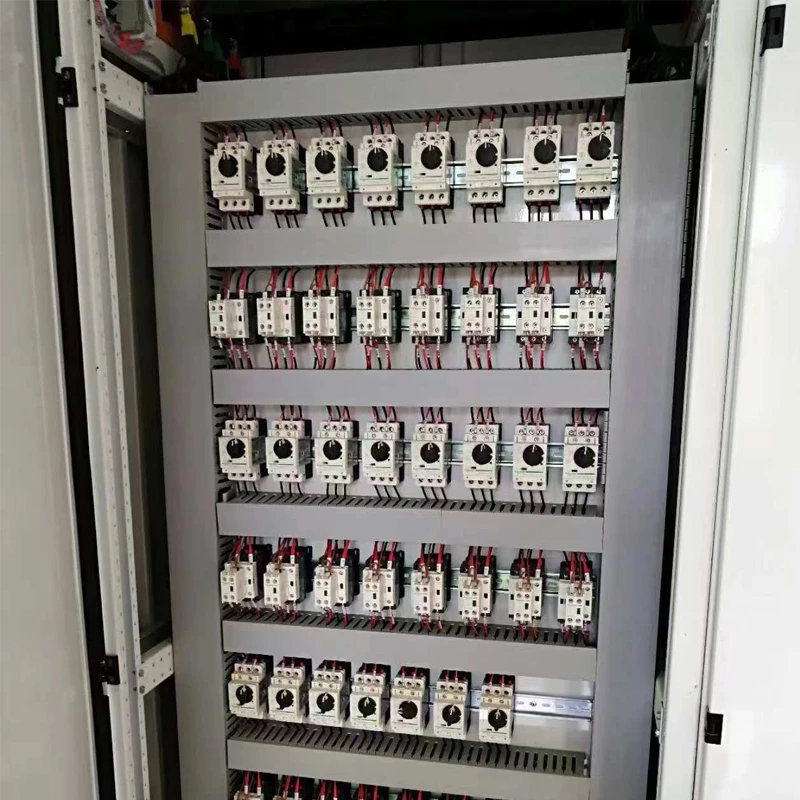
The Role of PLC in Robotics
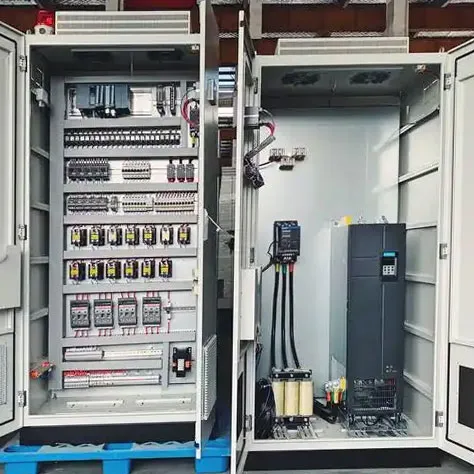
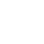
PLC is a specialized computer used for industrial automation to control manufacturing processes. It allows for the programming of complex sequences of operations, making it possible for robots to be adaptable to various tasks. In the case of four-axis welding robots, a PLC can manage the timing, speed, and path of the robotic arm during welding operations. This level of control ensures consistent weld quality while also optimizing production cycles.
Applications of Four-Axis Welding Robots
The applications of four-axis welding robots are diverse, spanning various industries. In the automotive sector, these robots are extensively used for welding car frames and components, providing high-speed, accurate welds that are vital for safety and durability. In the construction industry, four-axis welding robots are employed for fabricating steel structures, allowing for complex assembly with reduced manual labor.
Moreover, these robots find utility in the manufacturing of consumer goods, machinery fabrication, and even in the aerospace industry, where precision welds are critical
. The ability of PLC-based robots to integrate with other automated systems further enhances their versatility across numerous applications.robot de soldadura de cuatro ejes basado en plc

Advantages of Using Four-Axis Welding Robots
1. Increased Precision and Consistency One of the primary advantages of using four-axis welding robots is their ability to produce consistent results. The precision offered by robotic arms minimizes human error, ensuring that every weld meets the stringent quality standards required in industrial applications.
2. Enhanced Productivity Automation of the welding process significantly increases throughput. Robots can operate continuously, reducing downtime and increasing the overall production rate. This efficiency translates directly into cost savings for manufacturers.
3. Flexibility The adaptability of four-axis welding robots means they can be reprogrammed for different welding tasks. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in environments where product lines change frequently, allowing manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands.
4. Improved Safety Welding can be a hazardous task due to exposure to high temperatures, fumes, and electric shocks. By implementing welding robots, businesses can protect their workforce from potential injuries associated with manual welding tasks, thus promoting a safer workplace.
5. Integrative Capabilities PLCs can facilitate the integration of four-axis welding robots with other machinery and systems, creating a seamless production line. This integration aids in real-time monitoring and control, further enhancing efficiency and output quality.
Conclusion
The adoption of four-axis welding robots based on PLC technology represents a significant leap forward in automated manufacturing processes. Their precision, productivity, adaptability, and safety features position them as vital assets in today's competitive industrial landscape. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of these robots are expected to grow, ushering in new possibilities for innovative manufacturing solutions. By embracing automation through advanced robotics, industries can not only improve their operational efficiency but also pave the way for sustainable manufacturing practices that meet the challenges of the future.
-
Why Steel Mills Rely on FODA’s High-Temperature Cylindrical Roller Bearings?
NewsApr.10,2025
-
What is a Plain Bearing? A Complete Guide to Design & Functionality
NewsApr.10,2025
-
Thrust Ball Bearings vs. Tapered Roller Bearings: FODA’s Performance Comparison
NewsApr.10,2025
-
The Engineering Behind FODA Thrust Ball Bearings: Precision for High-Speed Applications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
No More Compromises: Get Precision-Engineered Custom Bearings Tailored to Your Exact Specifications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
In-Depth Analysis: Application Differences of Different Types of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
NewsApr.10,2025
Products categories