3 月 . 14, 2025 11:14 Back to list
The Future of PLC Control Systems: Trends in IoT and Smart Automation
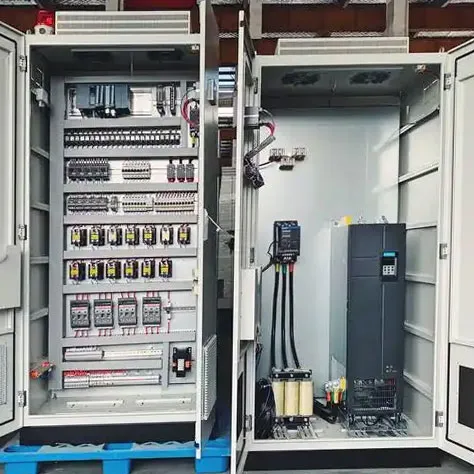
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have been the cornerstone of industrial automation for decades. However, with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart automation technologies, the role of PLCs is evolving rapidly. As industries adopt more interconnected and data-driven systems, PLCs are becoming smarter, more integrated, and capable of handling complex tasks beyond their traditional applications. This article explores the future of PLC control systems and the emerging trends in IoT and smart automation that are reshaping industrial environments.

The Rise of IoT-Enabled PLCs
IoT, which refers to the network of physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to exchange data, is having a significant impact on PLC systems. In the past, plc control system operated in isolated environments where communication with other devices was limited. However, with the integration of IoT, PLCs are becoming central to a larger network of connected devices.
By connecting PLCs to IoT platforms, manufacturers can enable real-time data collection, remote monitoring, and predictive analytics. For example, sensors on production lines can send data directly to PLCs, which can then relay this information to centralized systems or cloud-based platforms. This level of connectivity allows for immediate action in response to performance issues, improving overall system reliability and reducing downtime.

Cloud Integration and Data-Driven Insights About PLCs
As cloud computing continues to gain traction across industries, the integration of plc programming with cloud platforms is increasingly common. Cloud-based systems provide vast storage capabilities and allow for scalable data processing that was once impossible with on-site PLCs alone. Cloud-connected PLCs offer manufacturers the ability to store historical data, analyze trends, and gain insights from accumulated information.
With access to the cloud, PLCs can leverage advanced analytics tools and artificial intelligence (AI) to make intelligent decisions in real-time. For example, by continuously analyzing data from sensors and production machines, PLC systems can identify inefficiencies or anomalies, and recommend optimizations. The ability to make data-driven decisions allows industries to enhance performance, optimize energy usage, and reduce waste.

Edge Computing: A New Era of Localized Intelligence About PLCs
While the cloud is indispensable for big data analytics, edge computing is becoming a crucial complement to PLC systems in certain applications. Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, reducing latency and bandwidth issues associated with sending large amounts of data to the cloud.
For PLC systems, this means that certain computations can occur locally, enabling faster response times and enhanced control. By processing data on-site, edge computing can handle real-time decision-making without relying on a cloud connection. In industries where low latency is critical, such as automotive manufacturing or oil and gas, this localized intelligence can ensure that PLCs operate efficiently and responsively.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in PLC Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into PLC control systems to elevate their functionality beyond simple automation. These technologies enable PLCs to learn from data, adapt to changing conditions, and optimize processes in ways that were not previously possible.
For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data collected by PLCs to predict equipment failures before they occur. This predictive maintenance capability minimizes downtime and extends the life of machinery. AI-driven PLCs can also adjust operating parameters in real time to optimize energy consumption, reduce operational costs, and improve overall production efficiency.
The combination of AI, ML, and PLC systems opens the door to smarter, more autonomous industrial environments. As these technologies continue to mature, the ability to perform complex tasks such as quality control, process optimization, and resource allocation will become a standard feature of PLC systems.
The Importance of Cybersecurity in Smart PLC Systems
As PLCs become more connected to IoT networks and the cloud, the importance of cybersecurity grows exponentially. With increased connectivity comes the risk of cyberattacks, and PLCs are often vulnerable targets in industrial control systems. The potential consequences of a breach—such as data theft, system shutdowns, or even physical damage to machinery—can be catastrophic.
To address this concern, the future of PLC systems will place a greater emphasis on robust cybersecurity features. Manufacturers are already implementing advanced encryption methods, secure communication protocols, and multi-layered security strategies to protect PLCs from cyber threats. Additionally, regular software updates and vulnerability testing will be integral to ensuring that PLC systems remain secure in increasingly connected environments.
The Role of 5G in PLC Control Systems
5G technology is set to revolutionize the industrial landscape, and PLC control systems will be no exception. The ultra-low latency, high-speed data transfer capabilities of 5G networks make them ideal for real-time control and communication in industrial settings. For PLCs, 5G will enable faster data exchange between devices, machines, and control systems, significantly enhancing the responsiveness of automation processes.
With 5G, PLCs will be able to connect to a greater number of devices simultaneously, creating a more flexible and scalable automation ecosystem. For industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, where real-time data and immediate responses are critical, 5G-powered PLC systems will unlock new levels of efficiency and productivity.
The Evolution of Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) About PLCs
As PLCs become more sophisticated, their interfaces are evolving as well. The traditional Human-Machine Interface (HMI), which was often limited to basic control panels or screens, is now being replaced with more intuitive, interactive, and mobile-friendly solutions. Touchscreens, voice commands, and augmented reality (AR) applications are being integrated into HMI systems to allow operators to interact with PLCs more easily and effectively.
These advancements improve the user experience, making it simpler to monitor, adjust, and control automated processes. In addition, mobile HMIs enable remote access to PLC systems, allowing operators to manage processes from anywhere, whether on the factory floor or at home.
-
Why Steel Mills Rely on FODA’s High-Temperature Cylindrical Roller Bearings?
NewsApr.10,2025
-
What is a Plain Bearing? A Complete Guide to Design & Functionality
NewsApr.10,2025
-
Thrust Ball Bearings vs. Tapered Roller Bearings: FODA’s Performance Comparison
NewsApr.10,2025
-
The Engineering Behind FODA Thrust Ball Bearings: Precision for High-Speed Applications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
No More Compromises: Get Precision-Engineered Custom Bearings Tailored to Your Exact Specifications
NewsApr.10,2025
-
In-Depth Analysis: Application Differences of Different Types of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
NewsApr.10,2025
Products categories